Revitalize the Amazon: Small-scale Farmers are Crucial Players
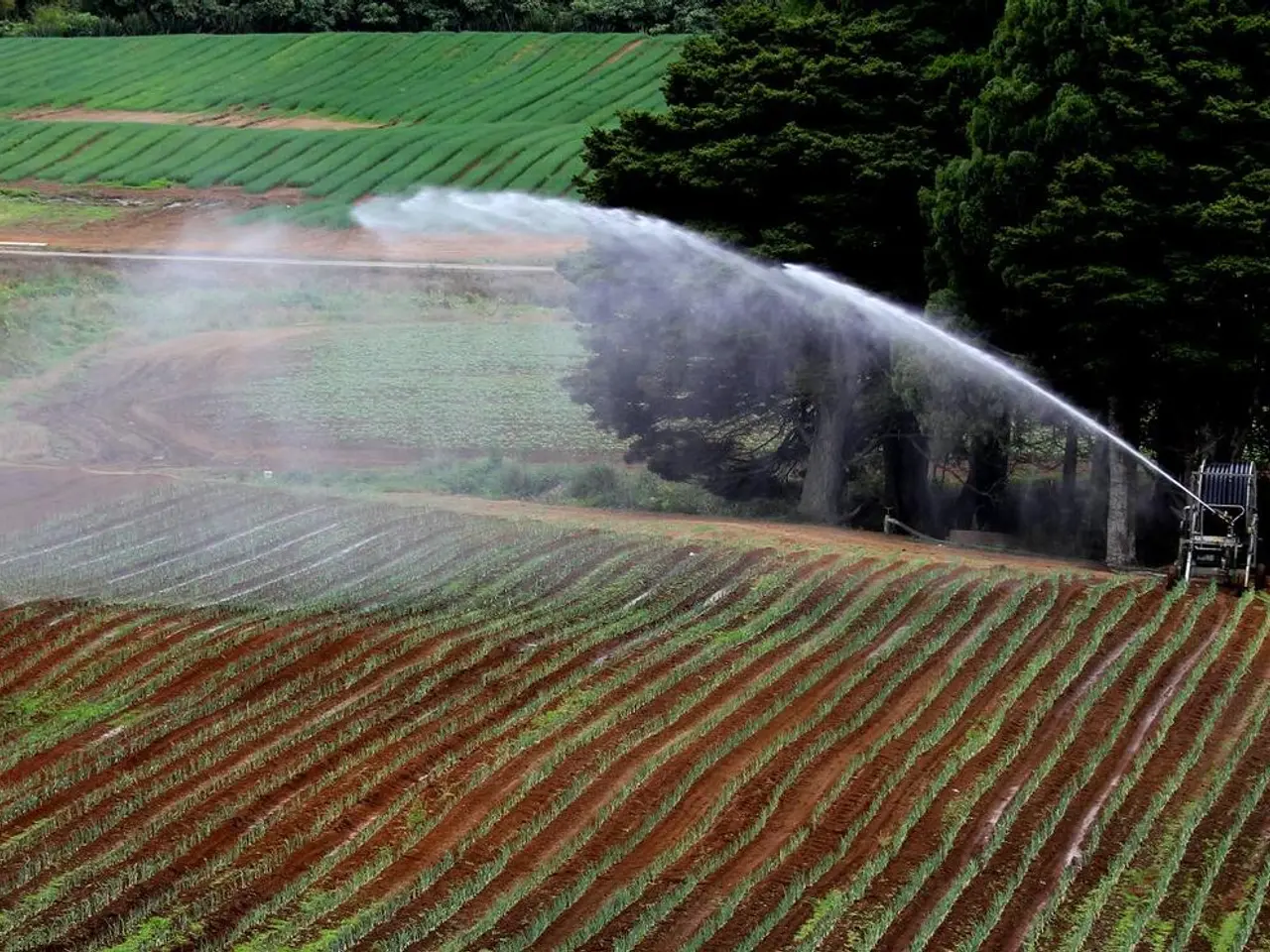
In a significant move towards combating deforestation in the Brazilian Amazon, Amazon Inc. has partnered with The Nature Conservancy (TNC) to promote agroforestry systems among local farmers in Pará, a region known for its pristine native vegetation, four times the size of the United Kingdom and home to 9% of the world's tropical forest.
The partnership aims to provide a more sustainable source of income for the 3,000 local farmers in Pará by growing and selling agroforestry products such as cocoa beans. By integrating trees with crops and livestock, this approach not only restores forest cover and maintains biodiversity but also improves livelihoods by diversifying income sources while reducing pressure to clear native forests.
Many families in Pará view clearing forestland for agriculture as the most rational business decision due to limited options. However, a lack of income alternatives and technical assistance is another key cause of deforestation in the region. The partnership between Amazon Inc. and TNC intends to address these issues by offering technical assistance and income alternatives to the farmers.
The collaboration also aims to demonstrate that deforestation and agricultural production can be decoupled. This is crucial, as agricultural production accounts for about 33% of the deforestation in Pará, with 2020 seeing the highest rates across the 360,000 small farms in the state.
TNC, with its 20-year history of working in the Amazon, will likely provide training, financial incentives, and technical assistance to help farmers adopt agroforestry models that combine native tree species with productive crops. Such programs also contribute to climate mitigation by enhancing carbon sequestration and protecting biodiversity.
Moreover, the partnership may work on monitoring and reporting deforestation impact and promoting policies supportive of agroforestry and forest conservation in the region. While the exact tactics of this specific partnership are not outlined in the available documents, these are established measures commonly implemented by conservation partnerships tackling deforestation and promoting agroforestry in the Amazon.
The partnership between Amazon Inc. and TNC is part of a larger effort to finance and implement nature-based solutions, including agroforestry, sustainable land management, and forest restoration, to combat deforestation in the Brazilian Amazon. This effort includes advocating for legal and financial frameworks that incentivize protecting and restoring forest landscapes rather than clearing them.
In conclusion, the partnership between Amazon Inc. and TNC represents a significant step towards promoting sustainable agriculture and combating deforestation in Pará, Brazil. By providing local farmers with the tools and resources they need to adopt sustainable practices, this partnership has the potential to make a substantial impact on the region's environment and economy.
- The collaboration between Amazon Inc. and The Nature Conservancy (TNC) in environmental-science focuses on climate-change mitigation, as they aim to demonstrate that deforestation and agricultural production can be decoupled in Pará, Brazil, by promoting agroforestry systems among local farmers.
- Besides offering technical assistance and income alternatives to 3,000 local farmers, the partnership also intends to finance and implement nature-based solutions like agroforestry, sustainable land management, and forest restoration to combat deforestation in the Brazilian Amazon.
- Technology plays a key role in the partnership, as TNC will likely provide training, financial incentives, and technical assistance to help farmers adopt agroforestry models that combine native tree species with productive crops, which also contribute to climate mitigation by enhancing carbon sequestration and protecting biodiversity.